info@chinaadventure.org
86-18008011324
Search
Tibet is a dream place for many travelers, but due to the high altitude, before visiting Tibet, try to get as fit and healthy as possible, both physically and psychologically. Visitors having record of heart, lung, other organ problems or anemia should consult their doctor before making the decision to visit Tibet. If you want to know more Tibet Travel Tips, here is the most detailed Tibet travel guide.

Altitudes of the Main Regions in Tibet
Cities /Counties Altitude (m)
Tsetang 3,500
Lhasa 3,650
Shigatse 3,836
Gyangtse 4,040
Tingri 4,300
Nyingchi 3,000
Chamdo 3,240
Purang 3,700
Damxung 4,200
Pagri 4,300
Nagchu 4,507
Amdo 4,800
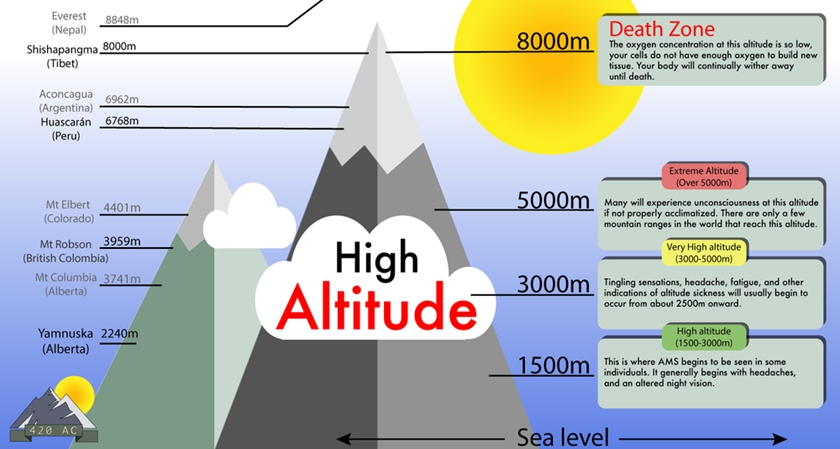
What is Altitude Sickness?
Place higher than 3,000 meters (9,843 feet) is usually defined as high altitude. Since most places in Tibet Autonomous Region are higher than this level, acute mountain sickness (AMS), also called altitude sickness is the biggest concern for most tourists visiting Tibet. AMS is common at high altitudes due to the decreasing availability of oxygen especially if Mt. Everest is on your travel list. Most people will experience different degrees of symptoms at high elevation. The occurrence of AMS is dependent on the altitude, the ascent rate and individual physical condition. However, please don't freak yourself out at most travelers will only suffer from slight symptoms and will get better on the 2nd day.


Symptoms of Altitude Sickness:
Symptoms of AMS include headache, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, loss of appetite and disturbed sleep. Most people will experience one or more AMS symptoms upon their arrival in Tibet. The symptoms will usually gradually decrease in severity during acclimatization, so it's not suggested to do strong exercises soon after you arrive in Tibet.


However, AMS can be very serious, with the most serious symptoms being High Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE) and High-Altitude Cerebral Edema (HACE), which can be fatal. Symptoms of HAPE include weakness, shortness of breath, even at rest, impending suffocation at night, and a persistent productive cough with white, watery, or frothy fluid. Symptoms of HPCE may include headache, ataxia, weakness, hallucinations, psychotic behavior, coma and loss of memory. Both approach and strike at night and can be fatal! If you don't feel well, please kindly contact your guide immediately and descend to a lower place to get treatment from hospital nearby.

How to Prevent the Altitude Sickness in Tibet?
1. Take good rest after your arrival. We normally don't arrange any sightseeing on the your arrival day so you can have enough time to take rest in hotel and get acclimatized.
2. When altitude sickness comes, do not panic. Please remember that most people will get it, especially for the first visit to Tibet. For most situations, it will fade away as long as you get proper rest.
3. You can take more sleep or take medicines following the doctor's advice. Before you go to Tibet, it's also OK to take some medicines in advance to get ready.
4. Try not to catch a cold. Coldness can be very troublesome if you are about to start the trip or if you are already here.
5. Please keep a good mood and be optimistic all the time.
6. Your high-altitude diet should consist primarily foods that are easy to digest, such as light soups, cereals, noodles, fruits and cooked vegetables.
7. "Climb high and sleep low." This is the mostly used tips by climbers. You can ascend to higher places but you can rest at a lower place to keep safe.
8. If you begin to show symptoms of moderate altitude illness, don't go higher until symptoms decrease (Don't go up until symptoms go down).
9. Keep in mind that different people will acclimatize at different rates. Make sure all of your party is properly acclimatized before going higher.
10.Stay properly hydrated. Acclimatization is often accompanied by fluid loss, so you need to drink lots of fluids to remain properly hydrated (at least 3-4 quarts per day).
11.Take it easy; don't over-exert yourself when you first get up. Light activity during the day is better than sleeping because respiration decreases during sleep, exacerbating the symptoms.
12.Avoid tobacco and alcohol and other depressant drugs including, barbiturates, tranquilizers, and sleeping pills. These depressants further decrease the respiratory drive during sleep resulting in a worsening of the symptoms.
13.Eat a high carbohydrate diet (more than 70% of your calories from carbohydrates) while at altitude.
14.The acclimatization process is inhibited by dehydration, over-exertion, and alcohol and other depressant drugs.
15. We will provide oxygen supply during your trip in Tibet. If you need it, please feel free to tell our guide and he will help you accordingly.
we’ll reply you in 24 hours!
Copyright © 2012-2024 All Rights Reserved to chinaadventure.org